When do defects in software testing arise?
Because of the following reasons the software defects arise:
- The person using the software application or product may not have enough knowledge of the product.
- Maybe the software is used in the wrong way which leads to the defects or failures
- The developers may have coded incorrectly and there can be defects present in the design.
- Incorrect setup of the testing environments.
To know when defects in software testing arise, let us take a small example with a diagram as given below.
We can see that Requirement 1
is implemented correctly – we understood the customer’s requirement,
designed correctly to meet that requirement, built correctly to meet the
design, and so deliver that requirement with the right attributes:
functionally, it does what it is supposed to do and it also has the
right non-functional attributes, so it is fast enough, easy to
understand and so on.
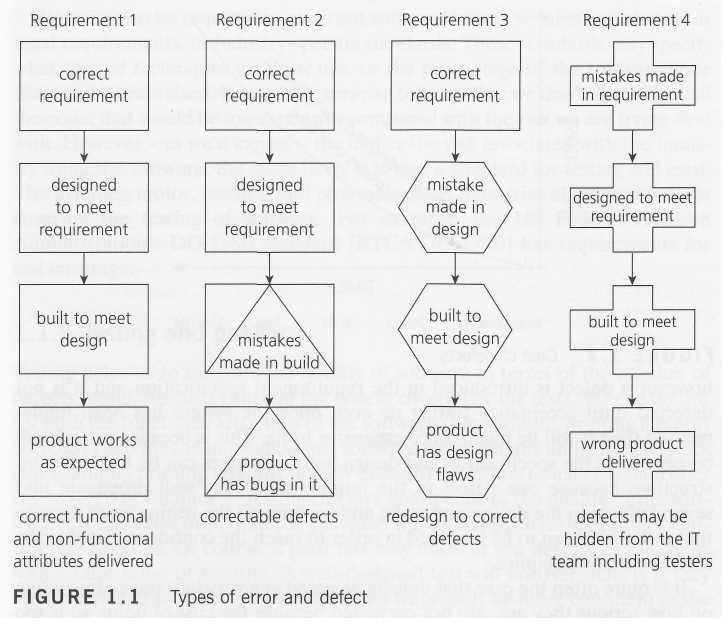
With the other requirements, errors have been made at different stages. Requirement 2
is fine until the software is coded, when we make some mistakes and
introduce defects. Probably, these are easily spotted and corrected
during testing, because we can see the product does not meet its design
specification.
The defects introduced in Requirement 3
are harder to deal with; we built exactly what we were told to but
unfortunately the designer made some mistakes so there are defects in
the design. Unless we check against the requirements definition, we will
not spot those defects during testing. When we do notice them they will
be hard to fix because design changes will be required.
The defects in Requirement 4
were introduced during the definition of the requirements; the
product has been designed and built to meet that flawed requirements
definition. If we test the product meets its requirements and design, it
will pass its tests but may be rejected by the user or customer.
Defects reported by the customer in acceptance test or live use can be
very costly. Unfortunately, requirements and design defects are not
rare; assessments of thousands of projects have shown that defects
introduced during requirements and design make up close to half of the
total number of defects.